- Inlet & Outlet Ports
- Driver Screw
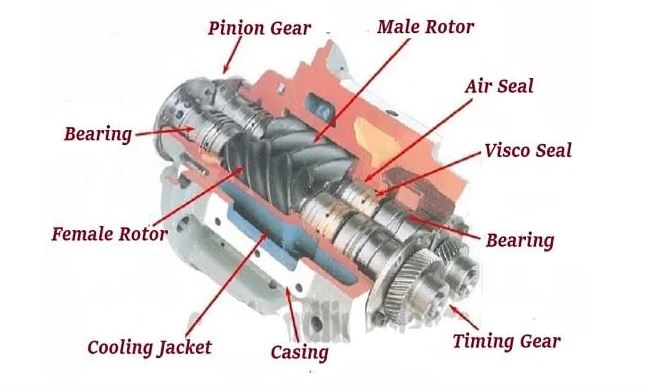
- Timing Gear
- Bearings
- Driven Screw
- Pressure Relief Valve
- Driving Shaft
Driver Screw
It’s a screw pump’s spinning component. The driver screw connects to the motor’s driving shaft. It aids in the consistent volumetric flow rate of fluid pumping. The timing gear is connected to one end, while the drive shaft is connected to the other.
The driven screw is rotated by the driver screw, which is powered by the motor’s driving shaft. It has a good fit with the driven screw. High-tensile steel is used to make this screw. The driver screw’s main job is to rotate the driven screw through a timing gear, which is an intermediary component.
Driven Screw
High-tensile steel metal is also used for the driven screw. Because of the movement conveyed by the timing gear, it rotates around its axis. It spins in the opposite direction as the driver’s gear. The clearance area of this screw is constant. This aids in catching water inside the restricted space.
The water volume decreases and travels toward the outlet port as the driver and driven screws move together. The fluid’s pressure rises as a result of this movement. It then discharges through the discharge/outlet port.
Timing Gear
The timing gear drives the driven screws in such a way that the female and male rotor assemblies do not make metal-to-metal contact. It establishes a link between the driver and driven screws. The driver screw rotates the timing gear, which then transmits that rotation to the driven screws. It drives screws in this manner. Even if the pump is turned off for a short time, it guarantees that no such connections are made.
Inlet & Outlet Ports
The intake and exit ports of a screw pump are distinct. The water is sucked into the pump through the intake port, and it is discharged through the output port. When the pump ultimately stops, the inlet and output are designed to ensure that there is enough liquid medium. This aids in the delivery of the pump’s initial liquid medium. As a result, the suction tube should not dry out quickly, even if it is empty or dry.
Pressure Relief Valve
Screw pumps are a type of positive displacement pump that builds pressure even while the outlet is closed. This builds up pressure, which can lead to major problems including pump internal part damage and harm to the pump operator. As a result, every positive displacement pump has a relief valve to safeguard the pump, the operator, and any associated gear. Extra pressure is returned to the intake using this valve. Recirculating the exit fluid is another well-known method of reducing extra pressure.
Bearings
During pump operation, the top bearings of a vertically mounted screw pump sustain heavy loads as well as axial and radial stresses. As a result, the load on the lower bearings is minimal.
The bottom bearing’s primary function is to keep the pump’s components aligned. Water screw pumps, roller bearings and slide bearings mounted in parallel, on the other hand, they have relatively low loads. This is due to the fact that the generated radial and axial forces are opposed and cancel one another out.
Driving Shaft
The driving shaft links the pump assembly to the drive motor. This connection is made possible by the use of the proper set of flexible couplings.
This driving shaft is a critical component of many types of pumps, and it goes from side to side to ensure the driver screw’s operation. The driving shaft is secured by a set of bearings that fit in the axial direction in such structures. As a result, accurate driving shaft alignment is critical to preserve the pump’s service life and bearings.
Characteristics of screw pump
Advantages
- These pumps are easy to maintain.
- Progressive cavity pumps can be used for all fluids
- It can be dried up
- It has a compact structure
- These pumps provide constant and non-pulsating fluid flow
- These have a quiet operation
- The pump can produce greater volumetric efficiency
- High reliability
- Self-priming capability
- High robustness
- The progressive cavity pump does not pump contaminants in the fluid
- It has frictionless rotation
- With a progressive cavity pump, you can also pump high viscosity fluids without losing flow
- High resistance to water vapor and particles/dust
- Very high pumping speed
- No contamination of the pumped medium
- Frictionless rotation – eliminates rotor wear
- High efficiency due to internal compression
- Relatively low operating costs and maintenance requirements
- Inverter operation – easily optimized for process requirements – resulting in high energy efficiency
Disadvantages
- Installation costs for small industries are high.
- The pump requires gas ballast to transfer light gases quality
- Without gas ballast, the ultimate pressure and pumping speed of light gases (helium and hydrogen) are reduced
- cannot be scaled down to small pumping speeds below 50 m³/h; below approx. 100 m³/h multi-stage Roots or scroll pumps are used
Application of screw pumps
Screw pumps have become the standard solution for almost all industrial vacuum processes. Vacuum furnaces for brazing or sintering, metallurgical systems, and even steel degassing equipment have the advantage of dust-proofing and long service intervals. In food processing, food drying, food packaging and even freeze dryers tend to use oil-free progressive cavity pumps to avoid contamination of the pump oil with water or process debris. Large-scale coating like architectural glass coating machine use screw pump as a high vacuum pump rough pumping. Screw pumps are also ideal for the regeneration of large cryogenic pumps.
Many lubrication and hydraulic machines use screw pumps to supply oil for large machines.
Screw pumps are more helpful in pumping heavy oil. They even have the ability to pump higher flow rates and higher viscosity fluids.
These pumps are capable of pumping both liquids and gases. For this reason, these pumps are used in many pumping industries.
The pumps are also used in oil and gas, mining and manufacturing industries.
These pumps are used in the ceramic, chemical, paint, food and paper industries.
