Pump performance curve remains an attractive topic in all food, milk, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries, so in this post we provide important information on our two most popular styles - centrifugal and positive transfers.
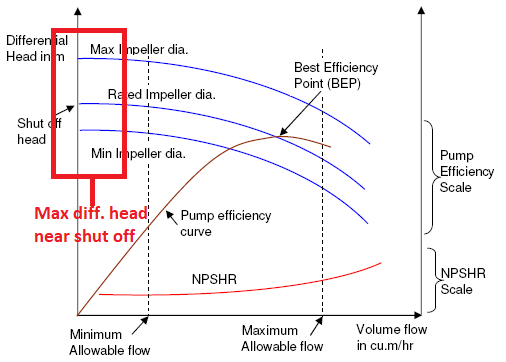
Also called the pump selection curve, the pump efficiency curve, or the pump performance curve, the pump curve graph gives you the information you need to determine the ability of the pump to produce a flow in conditions that affect performance. The reading pump curve accurately helps you choose the right pump based on application variables such as:
- Head (water pressure)
- Flow (the volume of liquid you have to move in a given time period)
This pump curve explanation also discusses variables such as:
- RPM
- Impeller size, as they related to pump performance
- Power
- Efficiency
- Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) in centrifugal and positive displacement pumps
Curves generally consist of information based on pressure, flow, horsepower, impeller trim, and Net Positive Suction Head Required (NPSHr).
Centrifugal pump curves are very useful because it showcase pump specifications based on head (pressure) produced by the pump and medium flow rate through the pump. Flow rates depend on pump speed, impeller diameter, and head.
WHAT IS HEAD?
The head is the height of the place of the pump can increase the water straight up. Water creates pressure or resistance, at a predictable level, so we can calculate the head as a differential pressure that must be resolved by the pump to increase water.
WHAT IS TOTAL DYNAMIC HEAD?
While pump curves help you select the right pump for the job, you first have to know the total dynamic head for the application.
Total Dynamic Head (TDH) is the amount of head or pressure on the suction side of the pump (also called static lift), plus the total of 1) height that a fluid is to be pumped plus 2) friction loss caused by internal pipe roughness or corrosion.
WHAT IS NPSH?
NPSHr is the minimum amount of pressure required on the suction side of the pump to avoid cavitation, or the introduction of air into the fluid stream. NPSHr is determined by the pump. You always want NPSHa>NPSHr.
EFFICIENCY AND PERFORMANCE VARIABLES
A good pump efficiency means that the pump is not wasting energy to maintain the point of its performance. No 100% efficient pump, however, in work must be done to transfer fluids.
When choosing a combination of pumps and motors, consider not only the current total request but future demand to ensure your choice has the capacity to meet changes in requirements. For this reason, the pump size for performance variables rather than peak efficiency is general practice.
